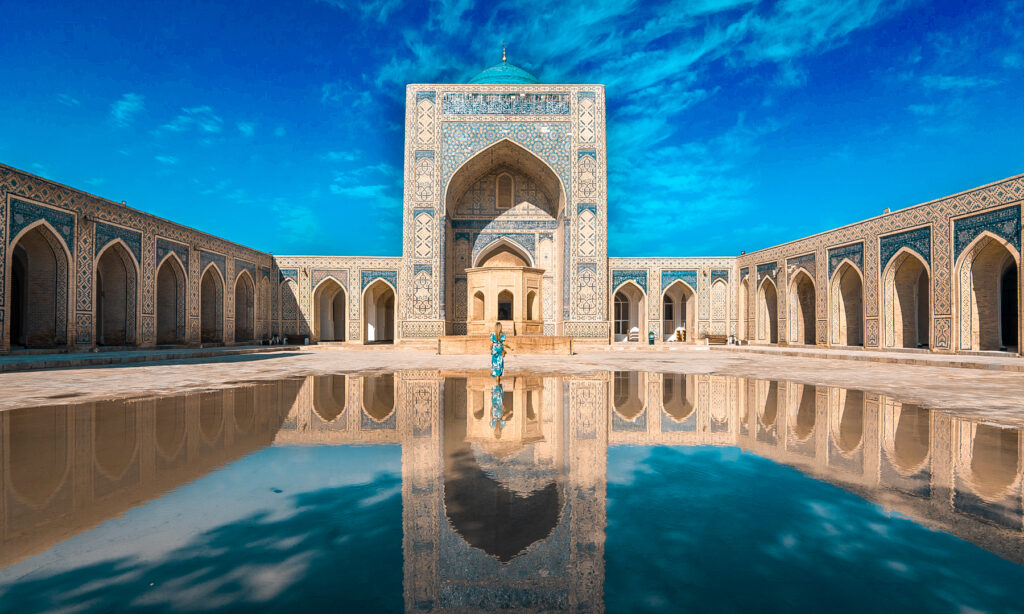
Introduction to the Silk Road: A Glimpse into Central Asia’s Historical Trade Routes
Embark on a fascinating journey as we explore the Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes that once connected East and West. Acting as a significant link, it wove together diverse cultures, economies, and regions from China to the Mediterranean Sea. This intricate web of paths was not merely a route for commerce but also a conduit for exchanging ideas, technologies, and cultural practices. The Silk Road has profoundly shaped the history and civilization of Central Asia, leaving an indelible imprint that still resonates today. Dive with us into the intriguing world of these historical trade routes and uncover the mysteries they hold.
Understanding the Origin and Evolution of the Silk Road
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes, has a rich and fascinating history that dates back to around 200 BC. It all began with the Chinese Han Dynasty’s exploratory missions, aiming to form alliances against the Xiongnu, a nomadic tribe. These missions led to the establishment of trade connections between China and the West, marking the inception of the Silk Road. Over time, it evolved and expanded, connecting various regions from China and India to the Mediterranean Sea. The Silk Road not only facilitated the exchange of goods like silk, spices, and precious metals, but also ideas, cultures, and technologies, significantly influencing the development of the regions involved. Understanding its origin and evolution helps us appreciate the profound impact it had on human history and civilization.
The Economic Significance of the Silk Road: From Local Trade to Global Exchange
The Silk Road, a vast network of trade routes stretching from China to the Mediterranean, played a significant role in shaping the economies of many countries in Central Asia. Initially, it facilitated local trade, allowing communities to exchange goods and ideas. However, its impact soon went beyond local boundaries, transforming into a global exchange system. This shift led to economic growth and cultural exchange on an unprecedented scale. The Silk Road became the backbone of economic progress, fostering trade relations between East and West and contributing to the prosperity of many ancient civilizations. Its existence underscores the power of trade and exchange in driving economic development and cultural integration.
The Cultural Impact of the Silk Road: How Trade Influenced Central Asian Society
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes that stretched from China to the Mediterranean, had a profound impact on Central Asian society. This bustling trade highway not only facilitated the exchange of goods like silk, spices, and precious metals, but also ideas, religions, and cultural practices. As merchants and travelers journeyed along these routes, they shared their beliefs, art, music, and even cuisines, leading to cultural diffusion. This cross-cultural exchange transformed societies, fostering a unique blend of traditions and customs. In essence, the Silk Road acted as a catalyst for globalization, connecting diverse civilizations, and shaping the cultural landscape of Central Asia.
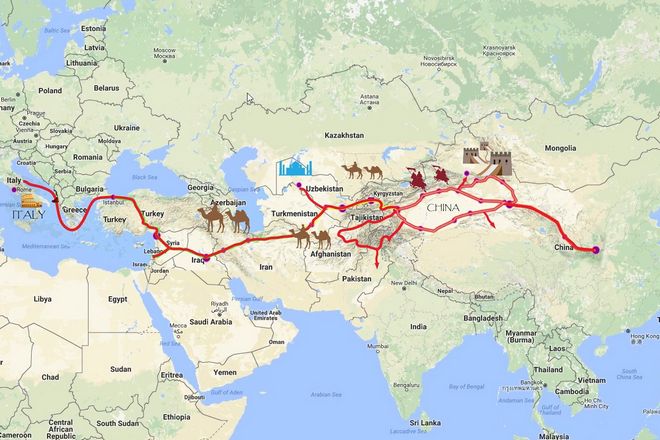
The Geography of the Silk Road: Exploring the Diverse Landscapes of Central Asia
The Silk Road’s geography is as diverse as the cultures it connected, stretching across the vast landscapes of Central Asia. From the towering, snow-capped peaks of the Pamir Mountains to the arid, windswept deserts of the Taklamakan, the Silk Road was a testament to human resilience and innovation. Traders, travelers, and explorers alike braved these harsh landscapes, carrying not just goods, but ideas, religions, and cultures along the way. The Silk Road’s geography played a pivotal role in shaping these journeys, with settlements often springing up around oasis towns or strategic mountain passes. Today, the remnants of these routes stand as a testament to the enduring legacy of the Silk Road and the rich tapestry of cultures it wove together.
The Silk Road and the Spread of Religion: Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity
The Silk Road, a network of ancient trade routes, played a significant role in spreading major religions such as Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity across Central Asia. Buddhism from India found its way to China, while Islam spread from the Arabian Peninsula to parts of China, India, and Southeast Asia. Christianity, too, traveled along these routes from the Mediterranean regions to as far as China. This exchange of religious beliefs and practices was not just a result of trade but also due to the movement of missionaries, pilgrims, and scholars. Thus, the Silk Road served as a vital conduit for religious dialogue and integration, shaping the cultural landscape of many regions in Central Asia.
Iconic Cities along the Silk Road: Samarkand, Bukhara and Khiva
Samarkand, Bukhara, and Khiva are iconic cities along the Silk Road that offer a glimpse into the rich history of Central Asia’s trade routes. Samarkand, known as the ‘Crossroad of Cultures’, boasts awe-inspiring architecture like the Registan Square. Bukhara, another gem, is filled with ancient madrasas, mosques, and markets that tell tales of the city’s vibrant past. Khiva, in China’s Xinjiang province, is the Silk Road’s westernmost city. Its lively Sunday market still thrives, echoing the buzz of traders from centuries ago. Exploring these cities gives you a sense of the cultural exchange and economic activity that once flourished along the Silk Road.

The Silk Road in the Modern World: Its Influence on Contemporary Trade and Diplomacy
The Silk Road, once a network of trade routes linking the East and the West, continues to shape modern commerce and diplomacy. Today, it inspires initiatives like China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), aiming to boost trade and stimulate economic growth across Asia and beyond. The Silk Road’s legacy is also seen in diplomatic relations, as countries along these routes collaborate to create mutually beneficial partnerships. This historical trade route, therefore, plays a significant role in shaping the global economy and fostering international relations in our modern world.
Unraveling the Mysteries: Archaeological Discoveries and Historical Records of the Silk Road
The Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West, holds numerous mysteries that archaeologists and historians are tirelessly working to unravel. The recent archaeological discoveries and recorded historical accounts of the Silk Road have shed light on the cultural, economic and political exchanges that took place over centuries. From unearthing artifacts that give us a glimpse into the lives of ancient traders, to deciphering historical texts that reveal the political dynamics of the time, these findings are enriching our understanding of this crucial trade route. The Silk Road’s secrets are slowly but surely being unveiled, offering fascinating insights into the rich history of Central Asia’s trade routes.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Silk Road and Its Influence on Central Asia Today.
In conclusion, the Silk Road’s enduring legacy continues to influence Central Asia today. Its age-old trade routes have shaped the region’s cultural, economic, and political landscape. Even today, Central Asia’s bustling bazaars, diverse cultural influences, and strategic geopolitical location are a testament to the Silk Road’s historic significance. It fostered cultural exchange and economic growth, turning the region into a melting pot of diverse civilizations. Today’s modern trade networks and diplomatic ties in Central Asia are deeply rooted in the vibrant history of the Silk Road, proving its influence is far from fading.
